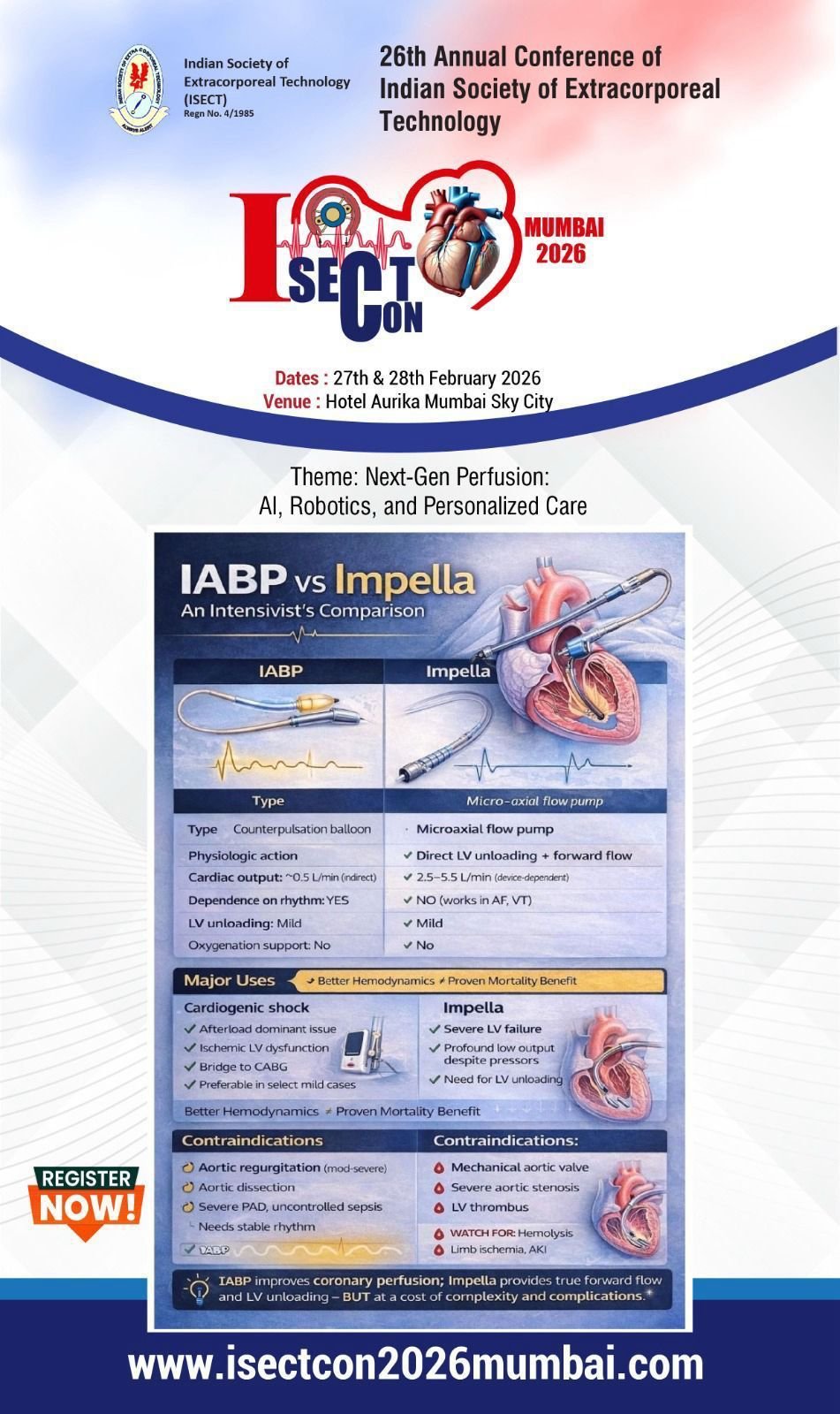
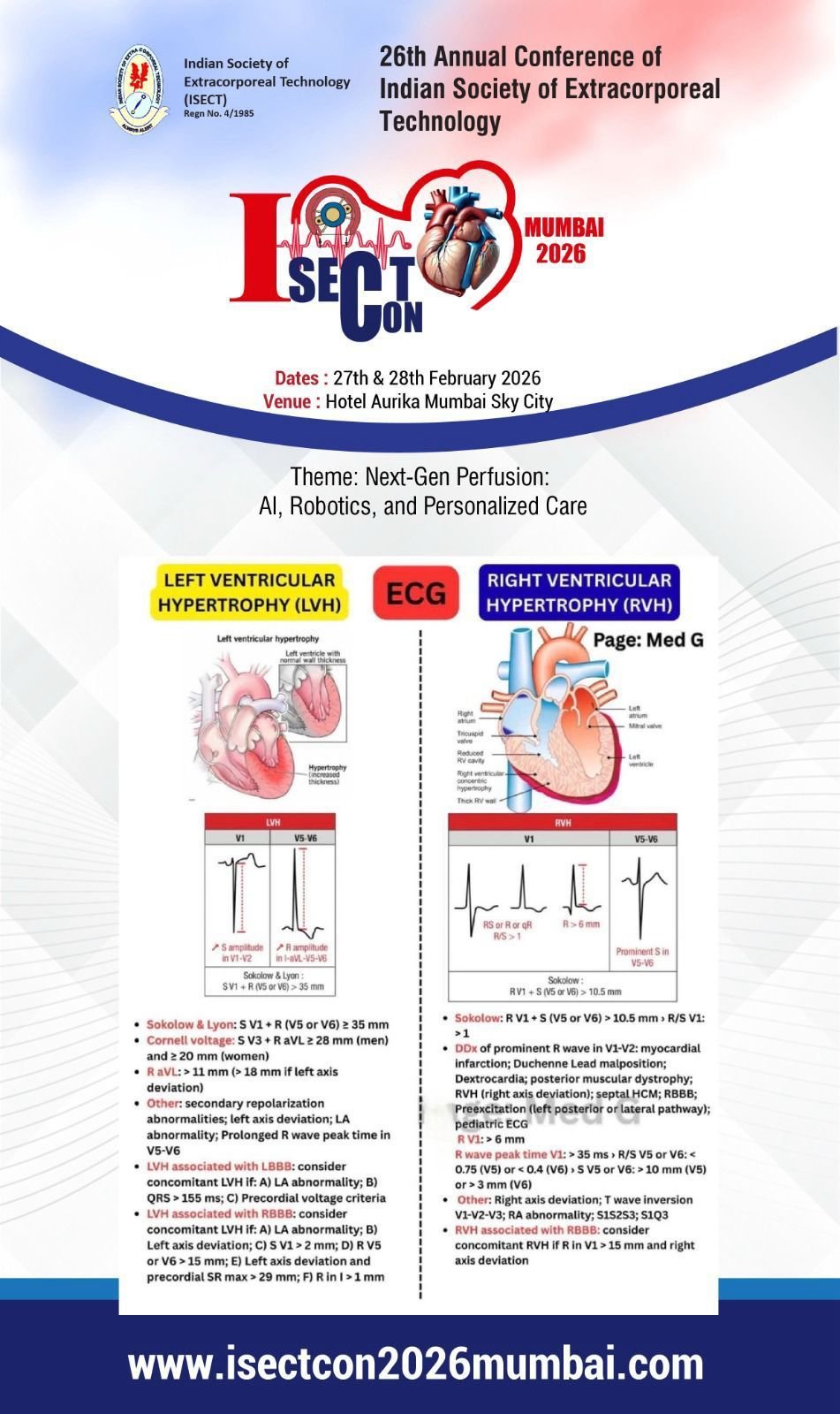
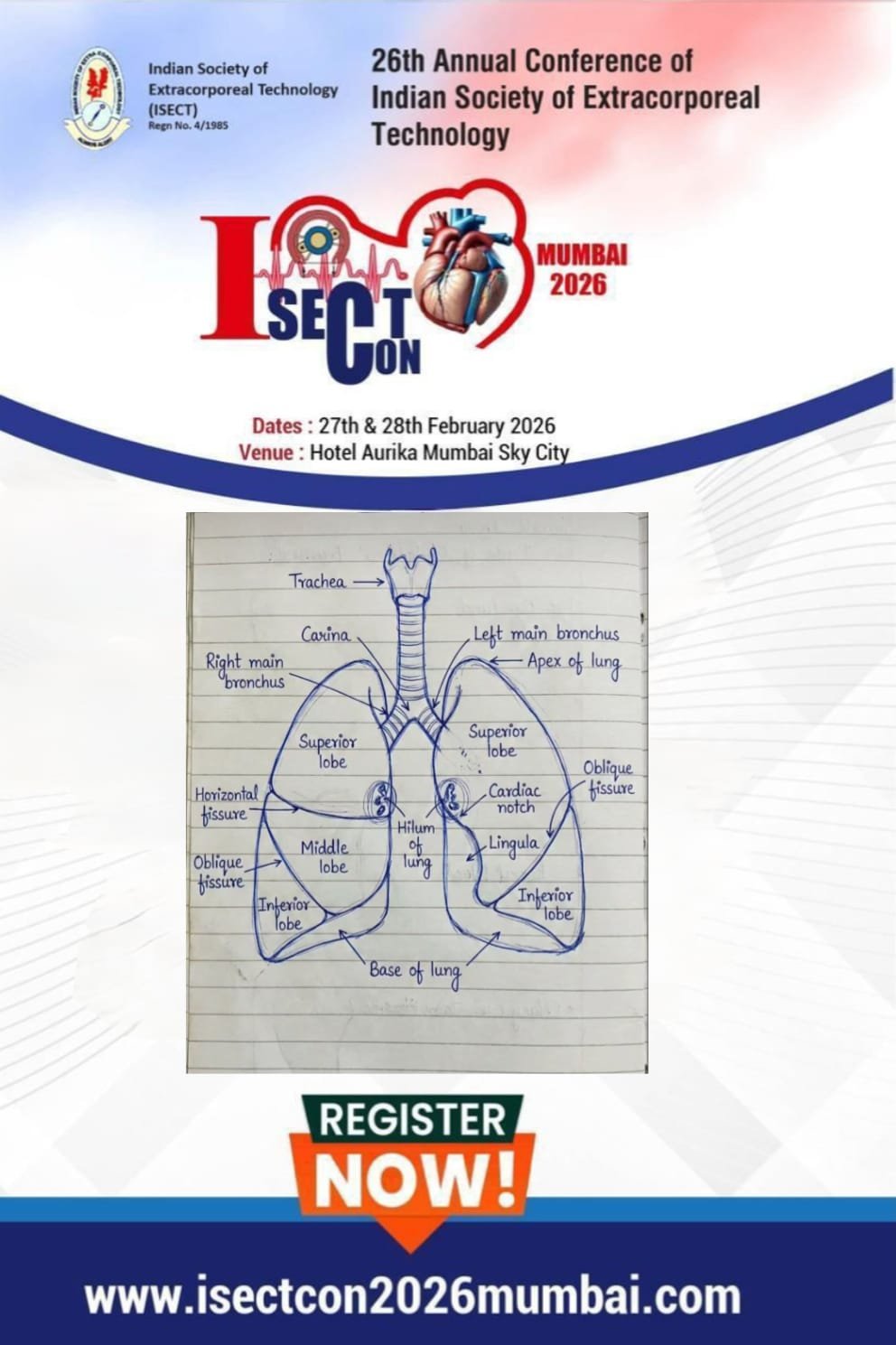
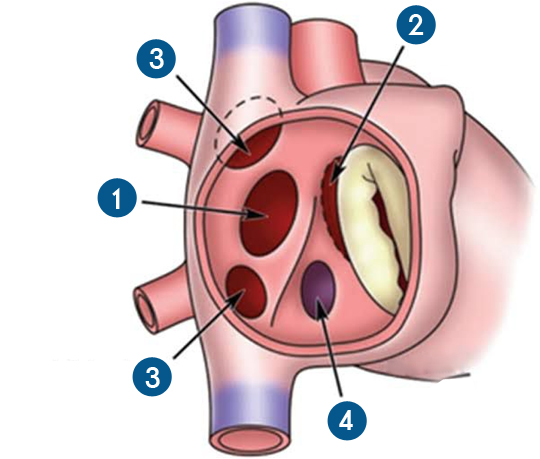
The procedure was introduced by William H. Muller, Jr. and J. Francis
Dammann, Jr. in 1951 and was initially used in an infant with ventricular septal
defect.
Pulmonary artery banding is a palliative surgical procedure used to decrease
excessive pulmonary blood flow. It is usually used for neonates and infants with
left-to-right shunts unable to withstand complete surgical correction.
Some indications include: single ventricle, multiple VSDs, Atrioventricular
Defects, Double Outlet Right Ventricle, Double Outlet Left Ventricle, Unrepaired
Transposition of the Great Arteries in neonates to prepare the left ventricle to
receive a higher systemic pressure load prior to Arterial switch procedure.